Flux bootstrap
How to bootstrap Flux for various Git providers
Version 2.6 of the documentation is no longer actively maintained. The site that you are currently viewing is an archived snapshot. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
The Flux project is comprised of a command-line tool (the Flux CLI) and a series of Kubernetes controllers.
To install Flux, first you’ll need to download the flux CLI.
Then using the CLI, you can deploy the Flux controllers on your clusters
and configure your first GitOps delivery pipeline.
The person performing the Flux installation must have cluster admin rights for the target Kubernetes cluster.
The Kubernetes cluster should match one of the following versions:
| Kubernetes version | Minimum required |
|---|---|
v1.31 | >= 1.31.0 |
v1.32 | >= 1.32.0 |
v1.33 and later | >= 1.33.0 |
The Flux CLI is available as a binary executable for all major platforms, the binaries can be downloaded from GitHub releases page.
With Homebrew for macOS and Linux:
brew install fluxcd/tap/flux
With Bash for macOS and Linux:
curl -s https://fluxcd.io/install.sh | sudo bash
With yay (or another AUR helper) for Arch Linux:
yay -S flux-bin
With nix-env for NixOS:
nix-env -i fluxcd
With Chocolatey for Windows:
choco install flux
To configure your shell to load flux
bash completions add to your profile:
. <(flux completion bash)
zsh,
fish,
and
powershell
are also supported with their own sub-commands.
A container image with kubectl and flux is available on DockerHub and GitHub:
docker.io/fluxcd/flux-cli:<version>ghcr.io/fluxcd/flux-cli:<version>The recommended way of installing Flux on Kubernetes clusters is by using the bootstrap procedure.
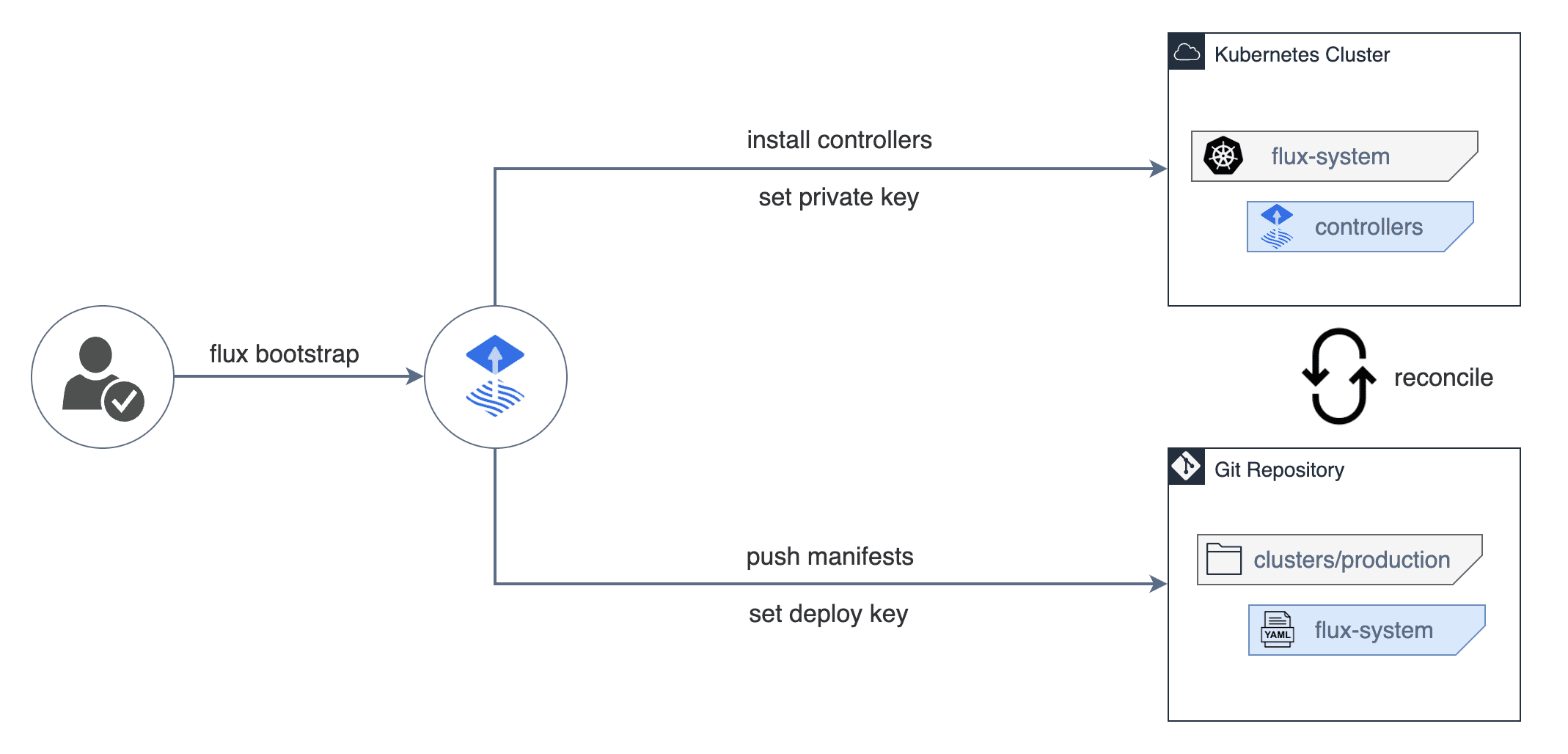
The flux bootstrap command deploys the Flux controllers on Kubernetes cluster(s)
and configures the controllers to sync the cluster(s) state from a Git repository.
Besides installing the controllers, the bootstrap command pushes the Flux manifests
to the Git repository and configures Flux to update itself from Git.
If the Flux controllers are present on the cluster, the bootstrap command will perform an upgrade if needed. Bootstrap is idempotent, it’s safe to run the command as many times as you want.
After running the bootstrap command, any operation on the cluster(s) (including Flux upgrades) can be done via Git push, without the need to connect to the Kubernetes API.
Flux integrates with popular Git providers to simplify the initial setup of deploy keys and other authentication mechanisms:
If your Git provider is not in the above list, please follow the generic bootstrap procedure which works with any Git server.
Various configuration options are available at bootstrap time such as:
Please see the bootstrap configuration section for more examples on how to customize Flux.
The bootstrap procedure can be implemented with Terraform using the Flux provider published on registry.terraform.io.
The provider offers a Terraform resource called flux_bootstrap_git that can be used to bootstrap Flux in the same way the Flux CLI does it.
Check out the examples available for the provider in the fluxcd/terraform-provider-flux repository.
The Flux Operator is an open-source project part of the Flux ecosystem that provides a declarative API for the lifecycle management of the Flux controllers.
The operator offers an alternative to the Flux CLI bootstrap procedure, with the option to configure the reconciliation of the cluster state from Git repositories, OCI Artifacts, or S3-compatible storage.
Install the Flux Operator in the flux-system namespace, for example, using Helm:
helm install flux-operator oci://ghcr.io/controlplaneio-fluxcd/charts/flux-operator \
--namespace flux-system \
--create-namespace
The Flux Operator can be installed using Helm, Terraform, OpenTofu, OperatorHub, and other methods. For more information, refer to the installation guide.
Create a
FluxInstance resource
named flux in the flux-system namespace to install the latest Flux stable version and configure the
Flux controllers to sync the cluster state from an OCI artifact stored in GitHub Container Registry:
apiVersion: fluxcd.controlplane.io/v1
kind: FluxInstance
metadata:
name: flux
namespace: flux-system
annotations:
fluxcd.controlplane.io/reconcileEvery: "1h"
fluxcd.controlplane.io/reconcileTimeout: "5m"
spec:
distribution:
version: "2.x"
registry: "ghcr.io/fluxcd"
artifact: "oci://ghcr.io/controlplaneio-fluxcd/flux-operator-manifests"
components:
- source-controller
- kustomize-controller
- helm-controller
- notification-controller
- image-reflector-controller
- image-automation-controller
cluster:
type: kubernetes
multitenant: false
networkPolicy: true
domain: "cluster.local"
kustomize:
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: "(kustomize-controller|helm-controller)"
patch: |
- op: add
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-
value: --concurrent=10
- op: add
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-
value: --requeue-dependency=5s
sync:
kind: OCIRepository
url: "oci://ghcr.io/my-org/my-fleet-manifests"
ref: "latest"
path: "clusters/my-cluster"
pullSecret: "ghcr-auth"
For more information on how to configure syncing from Git repositories, container registries, and S3-compatible storage, refer to the cluster sync guide.
The operator can automatically upgrade the Flux controllers and their CRDs when a new version is available.
To restrict the upgrade to patch versions only, set the distribution.version field to e.g. 2.6.x
or to a fixed version e.g. 2.6.0 to disable automatic upgrades.
The Flux Operator can take over the management of existing installations from the Flux CLI or other tools. For a step-by-step guide, refer to the Flux Operator migration guide.
For testing purposes you can install the Flux controllers without storing their manifests in a Git repository.
Install with flux:
flux install
Install with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/fluxcd/flux2/releases/latest/download/install.yaml
Install with helm:
helm install -n flux-system --create-namespace flux oci://ghcr.io/fluxcd-community/charts/flux2
How to bootstrap Flux for various Git providers
How to configure Flux during bootstrap
Upgrade the Flux CLI and controllers
How to uninstall the Flux controllers